IMPROVED EXTENDED XY ON-CHIP ROUTING IN DIAMETRICAL 2D MESH NOC
Prasun Ghosal and Tuhin Subhra Das
Bengal Engineering and Science University, Shibpur Howrah 711103, INDIA
ABSTRACT
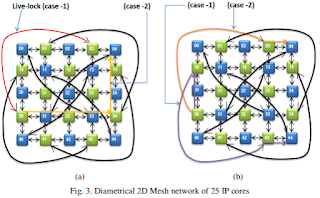
Network-on-Chip (NoC) is a new approach for designing the communication subsystem among IP cores in a System-on-Chip (SoC). NoC applies networking theory and related methods to on-chip communication and brings out notable improvements over conventional bus and crossbar interconnections. NoC offers a great improvement over the issues like scalability, productivity, power efficiency and signal integrity challenges of complex SoC design. In an NoC, the communication among different nodes is achieved by routing packets through a pre-designed network fabric according to some routing algorithm. Therefore, architecture and related routing algorithm play an important role to the improvement of overall performance of an NoC. A Diametrical 2D Mesh routing architecture has the facility of having some additional diagonal links with simple 2D Mesh architecture. In this work, we have proposed a Modified Extended 2D routing algorithm for this architecture, which will ensure that a packet always reaches the destination through the possible shortest path, and the path is always deadlock free.
KEYWORDS
NoC routing, Diametrical 2D mesh routing, On-chip communication, Extended XY routing
Original Source Link : http://aircconline.com/vlsics/V3N5/3512vlsics16.pdf